OCULAR ITCHING ASSOCIATED WITH ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS
THREE PIVOTAL PHASE 3 STUDIES IN 255 PATIENTS WITH
OCULAR ITCHING ASSOCIATED WITH ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS1-3
Study design*
Randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies in allergic conjunctivitis patients.
Objective
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of DEXTENZA for the treatment of ocular itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
Inclusion criteria
- History of allergic conjunctivitis
- Positive skin test for seasonal and/or perennial allergens
- Bilateral conjunctival allergen challenge (CAC) reaction
Study 1
N=73
DEXTENZA
(n=35)
Placebo
(n=38)
Study 2
N=86
DEXTENZA
(n=44)
Placebo
(n=42)
Study 3
N=96
DEXTENZA
(n=48)
Placebo
(n=48)
Primary Endpoint*
- Ocular Itching 3, 5, and 7 minutes post-Conjunctival Allergen Challenge on Day 8
Scores for patient-reported ocular itching using a 0 (none) to 4 (severe) scale.3
*Subjects received DEXTENZA or placebo vehicle insert bilaterally.2
DEXTENZA OFFERED SUSTAINED EFFICACY IN OCULAR ITCHING ASSOCIATED WITH ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS1,3
In each Phase 3 study, DEXTENZA patients experienced less ocular itching vs placebo on Day 8
- In all 3 studies, DEXTENZA resulted in lower mean ocular itching scores compared with the placebo group at all time points throughout the 1-month duration of the study.
- In 2 of 3 studies, a higher proportion of patients had statistically significant reductions in ocular itching on Day 8, at 3 minutes, 5 minutes, and 7 minutes post-challenge in the DEXTENZA group than in the placebo group.
- In Study 2, DEXTENZA did not meet the primary endpoint for reduction in ocular itching on Day 8.
- Patient-reported ocular itching scores on a 9-point scale from 0 (none) to 4 (severe).3
REDUCTION IN OCULAR ITCHING1 Study 1
| Time Period | DEXTENA (n=35) | Placebo (n=38) | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visit Day 8 Time Point | Least Square Means | Least Square Means | Difference (95% CI) |
| 3 minutes | 1.9 | 2.7 | -0.7 (-1.2, -0.3) |
| 5 minutes | 2.1 | 2.8 | -0.7 (-1.2, -0.3) |
| 7 minutes | 1.9 | 2.7 | -0.8 (-1.2, -0.4) |
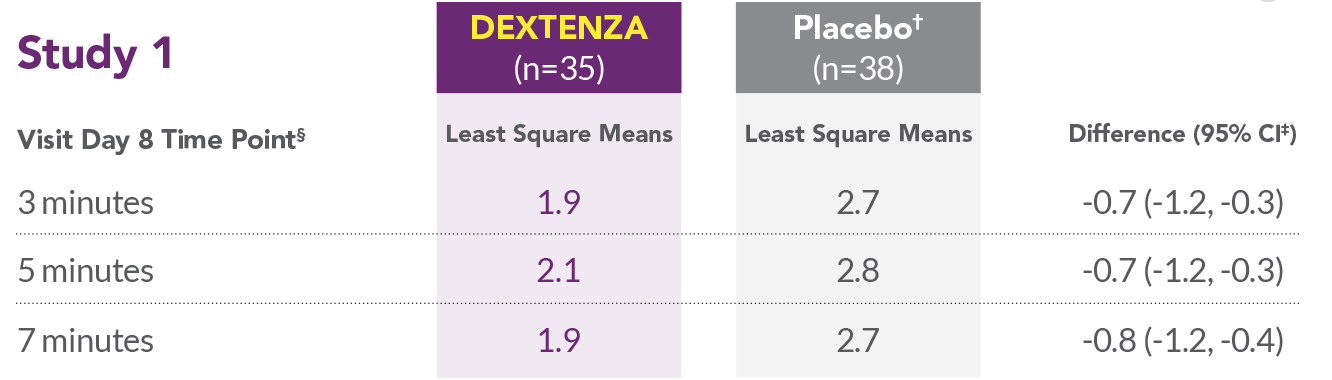
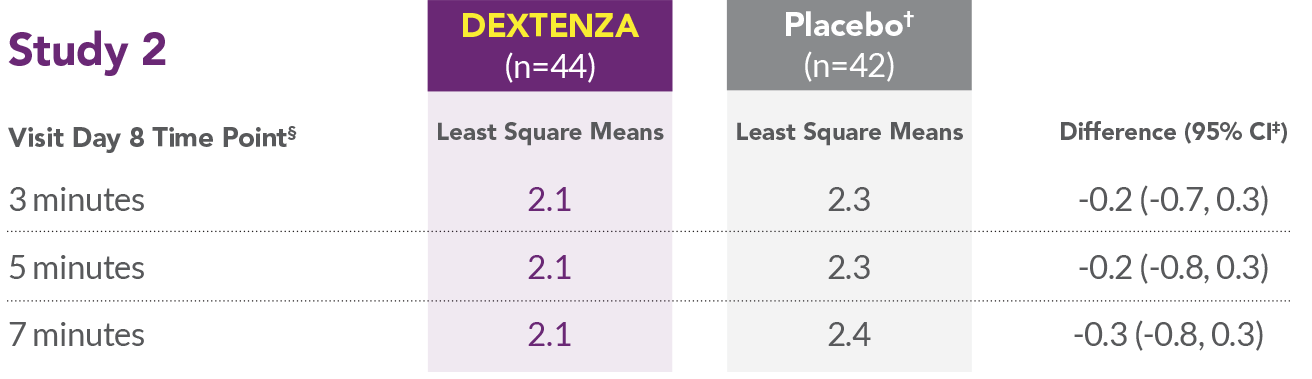
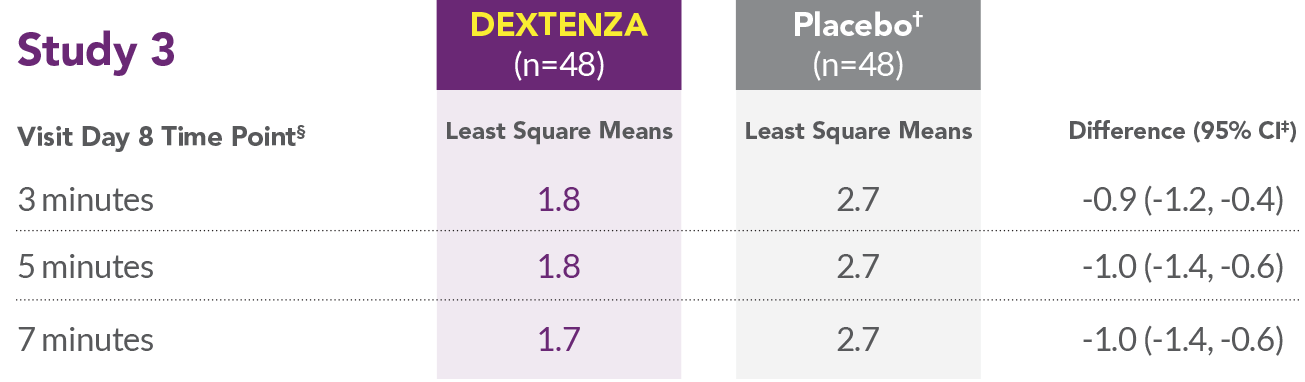
*Placebo was an insert containing no drug.
†CI = Confidence Interval.
‡Time post-conjunctival allergen challenge (CAC).
DEXTENZA WAS WELL TOLERATED IN OCULAR ITCHING ASSOCIATED WITH ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS1-3
Safety data pooled from one Phase 2 and three Phase 3 clinical trials1-3
Most common ocular adverse reactions in DEXTENZA patients (≥1%)1,2
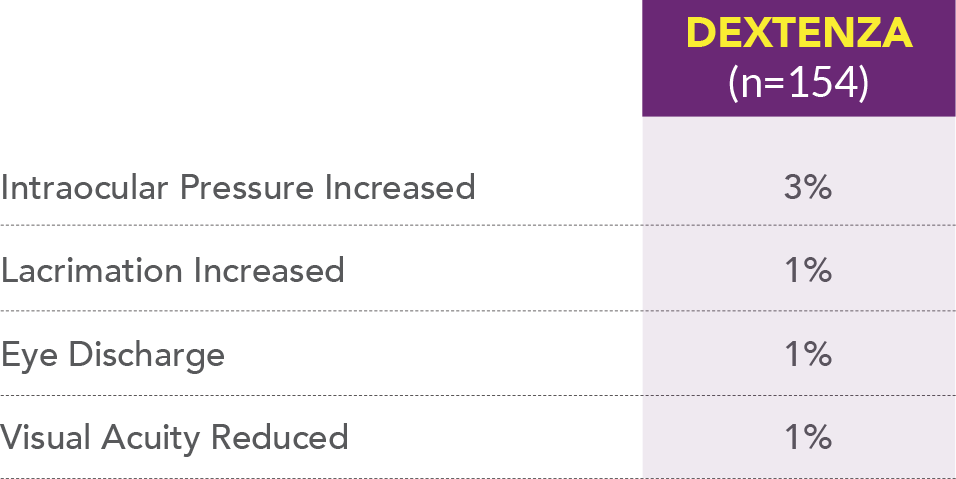
Most common non-ocular adverse reaction that occurred in patients treated with DEXTENZA was headache (1%).
References: 1. DEXTENZA [package insert]. Bedford, MA: Ocular Therapeutix, Inc; 2021. 2. Silverstein S, et al. Efficacy and Safety of an Intracanalicular Dexamethasone Insert (0.4 mg) for the Treatment of Allergic Conjunctivitis. Presented at: American Academy of Ophthalmology Annual Meeting; November 12-15, 2021; New Orleans, LA 3. Data on File 01333. Ocular Therapeutix, Inc.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
DEXTENZA is contraindicated in patients with active corneal, conjunctival or canalicular infections, including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella; mycobacterial infections; fungal diseases of the eye, and dacryocystitis.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Intraocular Pressure Increase – Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. Steroids should be used with caution in the presence of glaucoma. Intraocular pressure should be monitored during treatment.
Bacterial Infections – Corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard for secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection and enhance existing infection.
Viral Infections – Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex).
Fungal Infections – Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. Fungal culture should be taken when appropriate.
Delayed Healing – Use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation.
Other Potential Corticosteroid Complications – The initial prescription and renewal of medication order of DEXTENZA should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification, such as slit lamp biomicroscopy, and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after 2 days, the patient should be re-evaluated.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Ocular Inflammation and Pain Following Ophthalmic Surgery
The most common ocular adverse reactions that occurred in patients treated with DEXTENZA were: anterior chamber inflammation including iritis and iridocyclitis (10%), intraocular pressure increased (6%), visual acuity reduced (2%), cystoid macular edema (1%), corneal edema (1%), eye pain (1%), and conjunctival hyperemia (1%). The most common non-ocular adverse reaction was headache (1%).
Itching Associated with Allergic Conjunctivitis
The most common ocular adverse reactions that occurred in patients treated with DEXTENZA were: intraocular pressure increased (3%), lacrimation increased (1%), eye discharge (1%), and visual acuity reduced (1%). The most common non-ocular adverse reaction was headache (1%).
INDICATIONS
DEXTENZA is a corticosteroid indicated for:
- The treatment of ocular inflammation and pain following
ophthalmic surgery. - The treatment of ocular itching associated with allergic
conjunctivitis.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Disclaimer
Ocular Therapeutix, Inc. operates the Site and all rights thereto are owned and reserved by Ocular Therapeutix, Inc.
Any product/company information or other information published via the Site is given to the best of our (Ocular Therapeutix, Inc.) knowledge. All this information shall not, however, as far as legally permissible, create any guarantee or representation of any kind or any liability of Ocular Therapeutix, Inc. and shall not relieve the User from undertaking its own investigations and tests.
Without liability whatsoever Ocular Therapeutix, Inc. may without notice modify and/or discontinue operation of all or portions of this Site at any time in its sole discretion, and assumes no responsibility to update the Site.
ClosePLEASE READ THIS PRIVACY STATEMENT CAREFULLY.
Privacy is very important to us. We also understand that privacy is very important to you. This Privacy Statement (“Privacy Statement”) tells you how we protect and use information that we gather through this website located at dextenza.com.
Ocular Therapeutix is continually improving and adding new functionality and features to this Site. Because of these ongoing enhancements, changes in the law and the changing nature of technology, Ocular Therapeutix data practices will change from time to time. Accordingly, we reserve the right to update or modify this policy at any time without prior notice. If and when our data practices change, Ocular Therapeutix will post the revised policy on this page of our Site. Such changes to the Privacy Policy will become effective when posted. Your continued use of the Site after any changes or revisions to this Privacy Policy shall indicate your agreement with the terms of such revised Privacy Policy. We encourage you to check this page frequently by clicking on the Privacy Policy link on any page of our Site. By using this Site, you agree to the terms of this Privacy Statement. Please read our Terms of Use to understand the general rules about your use of this Site. Except as written in any other disclaimers, policies, terms of use, or other notices on this Site, this Privacy Statement and the Terms of Use are the complete agreement between you and Ocular Therapeutix with respect to your use of this Site. You may be subject to additional terms that may apply when you access particular services or materials on certain areas in this Site, or by following a link from this Site.
INTRODUCTION
The information we receive, and how we use it, depends on what you do when visiting our Site. We collect and use your non-personal information (information that is not identifiable to you personally) differently than your personal information.
WHAT IS NON-PERSONAL INFORMATION?
Each time you visit this Site to read or download information, we may collect certain information about you from your computer. This information is collected from your computer’s web browser and may include information such as the following (“non-personal information”):
- the type of web browser software you use (for example, Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari , Microsoft Edge or Internet Explorer)
- the name of the domain from which you access the Internet
- the Internet address of the website from which you linked directly to our Site
- the date and time you access our Site
Your IP address may be used to help diagnose problems with the server that administers our website. Your IP address is used to gather broad demographic information and is stored as a partial identifier. We use cookies, when applicable, to deliver content specific to your interests and when applicable to save your password so you don’t have to re-enter it each time you visit our site. You may set your browser to refuse cookies. If you make that choice, please understand that you may not be eligible for any specials and / or promotions we may offer our Site’s users.
WHAT DOES OCULAR THERAPEUTIX DO WITH NON-PERSONAL INFORMATION?
We will use non-personal information to help us make our Site more useful to visitors and for other business purposes, including but not limited to development and improvement activities. We may prepare reports and other materials using non-personal information. Since these reports and materials contain no personal information, we may share them with others.
WHAT IS PERSONAL INFORMATION?
In some places on this Site you may have the chance to send us information about yourself. For example, the Site may include a survey or an e-mail form.
The information (“personal information”) that we collect if you fill out a registration form or survey, or when you ask us to, may include, for example:
- your name
- address
- e-mail address
HOW DOES OCULAR THERAPEUTIX USE PERSONAL INFORMATION?
By submitting personal information (such as your name, address, e-mail address, telephone number), you agree that we may keep a record of it and may use it to respond to your request in compliance with the FDA or other applicable requirements. We also may use your personal information to help us in our business, including but not limited to improving this Site and product development.
On occasion, Ocular Therapeutix may offer special programs, activities and promotions via the Site (“Special Programs”) that have specific terms, privacy notices and/or informed consent forms that explain how your personal information will be processed in connection with the Special Program (“Special Program Terms”). Some of these Special Programs may involve sharing of your personal information with a third party and you may be offered the opportunity to agree to or opt-out of the sharing of your personal information with such third party. However, in some instances, it may be necessary to agree to sharing with a third party in order to participate in a particular Special Program. If you consent/do not opt-out, we may share your information with the third party and the personal information you provide may be used by the third party in accordance with the Special Program Terms and any applicable third party policies/terms before participating.
You agree that we may use your personal information to mail or email information to you about Ocular Therapeutix and our products and services.
Please note that any information you send to Ocular Therapeutix via email, in a sign-up form or via the Internet is not completely secure. We take reasonable steps to protect the personal information provided via this site from loss, misuse and unauthorized access or disclosure. However, no Internet or e-mail transmission is ever fully secure or error free. Due to the nature of the Internet, there is a possibility that unsecured (unencrypted) email or Internet transmissions could be intercepted and read by third parties. Ocular Therapeutix assumes no responsibility for interception of confidential information or personal information (including in a resume or CV or a sign-up form) that you send in an unsecured (unencrypted) email message or other Internet transmission to and from this Site. Therefore, you should take special care in deciding what information you send to us via e-mail, in a sign-up form or via other Internet transmission. DO NOT SEND INFORMATION RELATING TO YOUR MEDICAL CONDITIONS OR THOSE OF A FAMILY MEMBER OR ANY OTHER SPECIFIC PERSONAL HEALTH INFORMATION VIA THIS SITE, AS OCULAR THERAPEUTIX CANNOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH INFORMATION SENT THROUGH THIS SITE. Please keep this in mind when disclosing any personal data to Ocular Therapeutix via the Internet.
IS OCULAR THERAPEUTIX EVER REQUIRED TO SHARE PERSONAL INFORMATION WITH THIRD PARTIES?
Except as otherwise written in this Privacy Statement, we will keep your personal information private and will not share it with others, unless the disclosure is necessary to:
- comply with a law or regulation, court order or other legal process
- protect our rights or property
- enforce our Terms of Use or this Privacy Statement
- protect someone’s health or safety.
WHAT HAPPENS IF THE PRIVACY STATEMENT CHANGES?
If we decide to make a significant change to our Privacy Statement, we will post a notice on the homepage of our Site for a period of time after the change is made.
WHAT ABOUT PRIVACY ON OTHER SITES?
This Site may contain links to other websites that are not owned, controlled, reviewed or monitored by Ocular Therapeutix. Please be aware that we are not responsible for the privacy policies of such other sites or how these sites operate or treat your personal information. We encourage you to be aware that when you leave this Site and to read the privacy policies and terms of use of each and every third party website that collects personally identifiable information.
ARE THERE SPECIAL RULES ABOUT CHILDREN’S PRIVACY?
We care about protecting the online privacy of children. This Site is not directed at individuals under thirteen (13) years of age, and Ocular Therapeutix does not intend to collect any personally-identifiable information from such individuals (including, but not limited to, a child’s name or e-mail address), unless otherwise stated at the time such information is collected.
If you think that we have collected personal information from a child under the age of 13, please email us at info@ocutx.com. This e-mail address is being protected from spambots, therefore, you need JavaScript enabled to view it. You may also send us a letter addressed to the following address by First Class Postage Prepaid U.S. Mail or overnight courier:
Ocular Therapeutix, Inc.
24 Crosby Drive
Bedford, MA 01730
Attn: Regulatory Department
HOW TO CONTACT OCULAR THERAPEUTIX
If you have questions or comments about this Privacy Statement, please send an email to info@ocutx.com. This e-mail address is being protected from spambots, therefore, you need JavaScript enabled to view it. You may also send us a letter addressed to the following address by First Class Postage Prepaid U.S. Mail or overnight courier:
Ocular Therapeutix, Inc.
24 Crosby Drive
Bedford, MA 01730
Attn: Regulatory Department
This Privacy Statement was last revised on October 11, 2017
CloseAre you a US Healthcare Professional?
This website is intended for US Healthcare Professionals only.

